Pneumonia: Can It Cause Lung Cancer?
There are some risk factors of lung cancer, and smoking is the leading risk factor. In fact, most patients are associated with cigarette smoking (either active smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke). Personal history of other lung diseases can have contribution to increase the risk, too. How about pneumonia? Can it cause lung cancer?
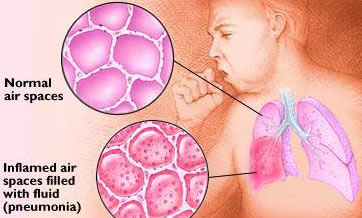
It is inflammation (swelling) due to infection that occurs in the tissues of one /both of the lungs. The infection usually attacks the air sacs (clusters of tinny air sacs at the end of breathing tubes in the lungs – see the picture below, credit to Mayo).
If you have pneumonia, your air sacs become inflamed and may fill with fluid or purulent material. As a result, you are likely to have difficulty breathing (such as shortness of breath) and cough with pus (purulent material).
 The symptoms can vary, from mild to serious. This is dependent on some factors like the age of patient, the overall health of patient, and the kind of ‘bacteria, fungi, or virus’ causing the infection. Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms can vary, from mild to serious. This is dependent on some factors like the age of patient, the overall health of patient, and the kind of ‘bacteria, fungi, or virus’ causing the infection. Other symptoms may include:
- Sweating, fever, or shaking chills.
- Fatigue.
- Chest pain, typically when taking a breath.
- Diarrhea that may also be followed with nausea and vomiting.
What is actually the exact cause of the disease? There are many types of germ that can lead to the disease. The most common are viruses and bacteria in the air.
The body has its own defense system to fight and prevent the infection. But sometime, these germs are more powerful than the immune system, even if you have a good general health.
It can affect anyone, but some people are at higher risk than others, these include:
- Children, especially those are age 2 or younger.
- Elderly people, especially those are older than 65.
- Some health conditions can also affect the risk. These include autoimmune disorders (particularly some that weaken the immune system like HIV /AIDS) and some chronic diseases (such as heart disease, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease),
- Being hospitalized, particularly if you are using a machine (like a ventilator) to help your breathe.
- Lifestyle factors, especially such as smoking. Some studies have shown that cigarette smoking can decrease and even damage the natural defense of the body in fighting against infection that causes pneumonia.
Pneumonia can be treated successfully with medication. Some treatments are available for coping, but it’s much better to prevent the disease. The good news, pneumonia is preventable. To reduce your risk, here are some general recommendations:
- There are vaccines to protect you from the infection of pneumonia and flu. See and talk with your doctor for more advice!
- Keep hygiene! Wash your hands regularly if necessary!
- If you are a smoker, consider quitting! Quitting can provide many health benefits, including reducing your risk of pneumonia and lung cancer.
- Boost your immune system and keep it strong by having a healthy-balanced diet, doing regular exercise, and getting adequate sleep every day!
Many times, it is treated successfully. However, some patients (particularly those in high risk groups) may develop some complications. These include
- Bacteria from the lung may spread to the bloodstream, causing infection to other parts of the body.
- Trouble breathing. In severe case, pneumonia may lead to difficulty breathing in enough O2 (oxygen).
- Pleural infusion (excess fluid accumulation around the lungs).
- If purulent material forms in a cavity of the lungs, this may lead to lung abscess.
It’s thought that previous diseases may increase the risk of developing cancer in the lungs. This is particularly true for a lung disease that has caused scarring in the lungs.
There are some types of lung cancer. But generally, these types are categorized into two main groups; small cell and non-small cell type. Small cell type is mostly found in smokers. Non-small cell type can occur in both smokers and non-smokers.
In addition, non small cell type has several sub-types. And when it comes to the risk of lung cancer associated with the previous lung disease, adenocarcinoma (a kind of non-small cell type) often takes attention which is also the most common subtype of non-small cell lung cancer.
But although some previous lung diseases increase the risk, this doesn’t necessarily mean that these diseases cause lung cancer! For instance, sometime lung cancer may be misdiagnosed for one of these lung diseases.
Furthermore, again smoking is still the leading risk factor. Lung cancer is also actually preventable. There are plenty of steps with lifestyle measures to prevent it. See also a comprehensive guide to prevent lung cancer in here!
According to a meta-analysis & pooled analysis of case-control researches, pneumonia may increase the risk of lung cancer by about 43-57 percent (including for smokers), and about 35- 36 percent in never-smokers.